If the term blockchain makes your eyes glaze over, you’re not alone. Often hyped but seldom fully understood, there’s a lot to learn about blockchain before you can evaluate its potential ROI for your company. That’s where blockchain 101 comes in handy, especially since research indicates that blockchain for supply chain management is here to stay.
Gartner predicted that “by 2023, blockchain platforms will be scalable, interoperable, and will support smart contract portability and cross chain functionality.” If that assessment and trends hold, supply chain-related applications will begin infiltrating industries in much bigger ways in just months. Some of the biggest blockchain breakthroughs will be in supply chain management. With more than 500 members in the Blockchain in Transportation Alliance (BiTA) and a hundred-plus participants in the TradeLens blockchain for ocean freight, the time is right for supply chain professionals to develop a deeper understanding of how they can apply this technology.
A Blockchain Tutorial for Supply Chain
The Global Supply Chain Institute dug into blockchain technologies, their benefit for supply chain management and how to get started evaluating blockchain ROI for your company in the white paper, “When Is(n’t) Blockchain Right?”
Below you’ll find a blockchain 101 for supply chain professionals. Consider it a bite-sized blockchain tutorial, drawn from the white paper, to help take the mystery and intimidation out of this transformative technology.
What is Blockchain?
We say blockchain, and you may hear Bitcoin. While cryptocurrency is blockchain’s most famous application, it’s not its only application.Which is fortunate, given the fluctuations and volatility of crypto these days. Think of it this way: while all cryptocurrency is blockchain technology, not all blockchain technology is cryptocurrency.
So, what is blockchain?
Blockchain is simply a shared digital ledger used to process, record and track transactions in a business network.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Think of blockchain literally as blocks and chains.
The Blocks
- Transactions in this ledger can take the form of a tangible asset, like a toaster, or an intangible asset, like the patent on a toaster.
- Once you record a transaction—a “block” of information— in the digital ledger,an address called a “hash” is created for each block.
- Everyone using the ledger validates each block of information as it enters the network.
The Chain
- Each block is connected to the one before and after it, making it impossible to remove a block without detection.
- The more blocks linked together, the stronger the chain.
- This chain is how blockchains create a shared ledger that all participants in the network can trust.
What Makes Blockchain So Secure?
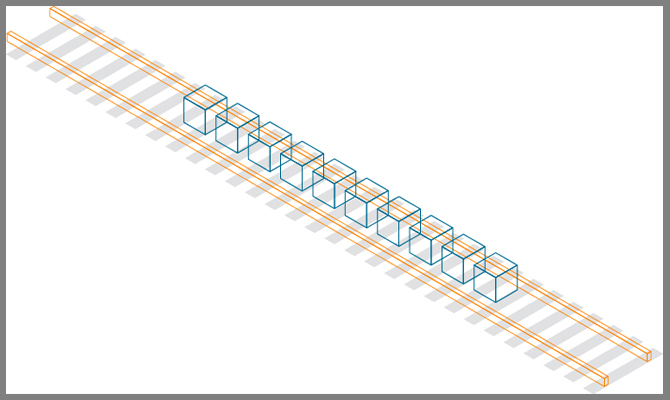
Let’s break this down with a quick visualization:
- Railroad ties = A block of data
- Track = The chain connecting one block to another
- Train = The applications that operate on top of the train tracks
A number of people must agree on where to place each railroad tie. They then place the track over the ties. The train runs over the tracks, connecting all the points along it. Theoretically, someone could move the railroad ties. But they couldn’t do that without removing the track—which would require agreement from others. This is why blockchain is said to be immutable.
What Types of Blockchain Exist?
There are three different types of blockchains: public, private and hybrid.
- Public: Any user can access and read the information using its unique identifier (i.e., barcode, QR code, RFID).
- Private: A limited number of users are given an access key.
- Hybrid: Elements of both (e.g. unlimited users but permissions restricting certain information).
The distinction between public, private and hybrid mostly boils down to permissions and the level at which they’re applied. That’s why you often hear private blockchains referred to as “permissioned” and public ones as “permissionless.”
What Can Blockchain Do for Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management uses blockchain in the same ways as explained above. No matter the application, industry or unique application, blockchain is all about secure information exchange. What could make blockchain so valuable to supply chain management is its ability to solve what is arguably the supply chain management problem.
- The Supply Chain Management Problem: The need to share information immediately and securely across wide networks with multiple parties, including competitors.
- The Blockchain for Supply Chain Solution: A shared ledger providing multiple participants in the supply chain the exact same information about transactions, from raw materials to a finished product at a customer’s doorstep.
- The Implications: Take a step back and think about that for a moment. All the technologies applied to digitizing supply chain, all the visibility and transparency tactics, and all the E2E supply chain strategies we’ve worked toward over decades have been trying to accomplish this goal: a verified source of truth across the entire supply chain that doesn’t open any member up to security issues.
Can blockchain really succeed where so many other approaches have struggled?
What Makes Blockchain Different?
You’ve heard the supply chain management panacea sales pitch before. Other distributed ledger technologies use independent computers to record, share and synchronize transactions. This creates a massive burden for data governance.Ensuring that information isn’t duplicated, disconnected, or inaccurate takes an exorbitant amount of time and centralized effort.
Blockchain democratizes data governance to provide verified data in a timely manner. That means better information faster and organized in a way that makes the most sense to users.
What does that mean for supply chain? Great agility. Great resilience. And blockchain’s major value point: great security.
When many partners or competitors must share information within an end-to-end supply chain, or need to execute commercial transactions in cases when trust is limited, blockchain can be a great solution.
How are Companies Currently Using Blockchain for Supply Chain?
Over the course of 18 months, the authors conducted research with industry-leading companies like Amazon, Mondelēz International. To them, they posed the question: “What is the ROI of blockchain?” The dozens of case studies and interviews appearing in this white paper will help supply chain management professionals understand how blockchain can be used, how organizations are already using it, and how to know if it will support their companies.
The most common way blockchain creates value in supply chain is through efficiency and consumer transparency.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Efficiency
- A large 3PL has initiated its own blockchain technology to minimize transit time, increase revenues and offer the customer shipment transparency.
- Blockchain in the supply chain provided by this 3PL would enable the shipments to quickly clear customs without the need for a paper trail.
Blockchain for Consumer Transparency
- In 2019, Nestlé launched its “Chain of Origin Coffee,” using Amazon’s blockchain technology to trace the original source of the coffee bean.
- By using blockchain technology, customers were able to trace coffee beans to their specific, originating farm.
It’s important to note that blockchain, like many emerging technologies, doesn’t gain its power in isolation. Blockchain becomes truly transformative when it forms part of a technology ‘stack’. Think of when a company deploys sensors (i.e., the industrial internet of things or IIoT) to capture in-transit data, feed the data to a secure blockchain, and allow AI/ML algorithms to interpret the data, potentially using high-performance computing to shorten turn-around time on simulations.
How Will Blockchain Impact Supply Chain Management?
There are two use cases that we believe blockchain will make a pivotal impact on in the near future: fragmented supply chains and smart contracts.
Use Case: Fragmented Supply Chains
- A company’s quest to become resilient and agile leads it to take on new production partners and expand its supply chain network.
- A previously tight-knit, trusted group turns into a large, unknown one almost overnight. At the second and third tier level, the supply chain network becomes even more complicated.
- The company needs a way for all supply chain partners to communicate in a secure, digital format.
- Blockchain technology provides the solution by coordinating the distributed network into a single communication tool with security restrictions.
Use Case: Smart Contracts
- A customer’s distribution center dips below the contractually determined inventory level.
- Managers notice the lapse and start a lengthy process to bring inventory levels back up.
- The effort to prevent such a situation ties up cash and DC space in supplementary supply.
- Smart contracts convert human-readable language, like legal contracts, into computer-readable language in a series of if-then statements.
- A smart contract prevents this situation by triggering an order to the manufacturer at the exact moment needed to keep inventory at a specific level.
- Implementation of smart contracts gives all participants confidence about where the product is and who owns it at any instance throughout the supply chain.
How to Know if Blockchain is Right For You?
Hopefully this blockchain 101 was a helpful step toward better understanding this technology. As with any technology, there is a right place, time and company profile for using blockchain. At the moment, a small 3PL might truly struggle to gain ROI from a blockchain investment if it’s building a platform from scratch.
So how do you know when the situation is right and how to start? Inside the full Global Supply Chain Institute white paper, you’ll find more in-depth information, along with a Blockchain Screener and a 15-question Decision-Support Framework to map out blockchain opportunities with your colleagues. Used together, these tools provide a structured and efficient approach to assessing the timing and extent of an investment in blockchain for your organization.
Find a full explanation of blockchain’s ROI for supply chain management and tools for screening use cases in the full GSCI white paper, available for free download below.